The return of steel
Steel tempering is a final heat treatment that is always applied after hardening. It consists of heating the hardened steel to a temperature below the critical point AC₁, maintaining and cooling generally in the air.
Heating temperatures are very different depending on the type of steel.
There are 4 basic types of heat treatment of steel: annealing, normalizing, hardening, and tempering.
Why is it necessary to return steel after hardening treatment?
After hardening, steel has an unstable, hard and brittle structure. The characteristics of mechanical strength and hardness are high, but the characteristics of plasticity and toughness are low
The tempering treatment is applied to steels that undergo physical transformations. Following this treatment, the unstable and fragile state changes to a more stable and less fragile state.
RETURN OF STEEL – PURPOSE OF APPLICATION:
– elimination or reduction of internal stresses in steel parts after hardening;
– transformation of the martensitic structure of the hardened parts into a more stable structure;
– reducing frailty;
– increasing tenacity.
The tempering temperature is chosen according to the mechanical characteristics imposed on the piece.
The hardness of the hardened part decreases with the increase of this temperature, and the toughness increases.
The duration of heating depends on the dimensions of the part and has the purpose of not creating internal tensions in the material.
Depending on the temperature, three types of returns are distinguished (see the table below).
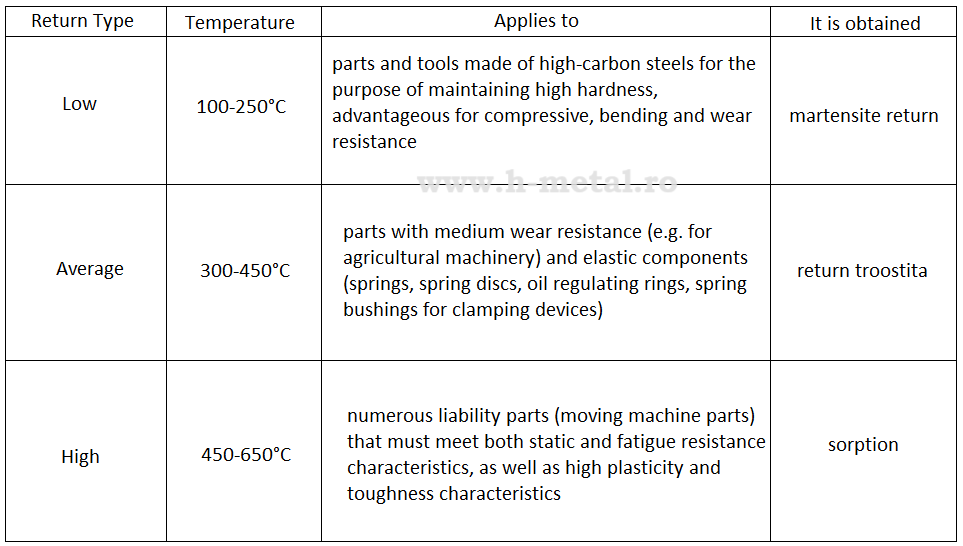
By low tempering, the aim is to reduce the residual stresses in the hardened parts, without decreasing their hardness.
High yield limits of the material of the treated parts, in order to ensure their good elasticity, are obtained after the medium tempering.
And following the high tempering treatment, a piece with high mechanical resistance and good toughness is obtained.
The tempering temperature influences the mechanical properties in that it determines the degree of dispersion of the carbides in the ferrite-carbide mixture.
Hardening and low recovery can be grouped into a single operation called self-returning hardening.
The high bounce is the most common of the three types detailed above.
Return cooling is done in air, except for alloy steels susceptible to brittleness on return, which from temperatures 550-650°C cool quickly in water.
H Metal sells a wide range of metallurgical products subjected to heat treatments.
To receive a concrete offer, please contact us at office@h-metal.ro.
<< Inapoi